- 【Alltruth Limited】Welcome to Alltruth Power(www.alltruthpower.com), We provide you professional power solutions.
- Make a call:138 5726 9602
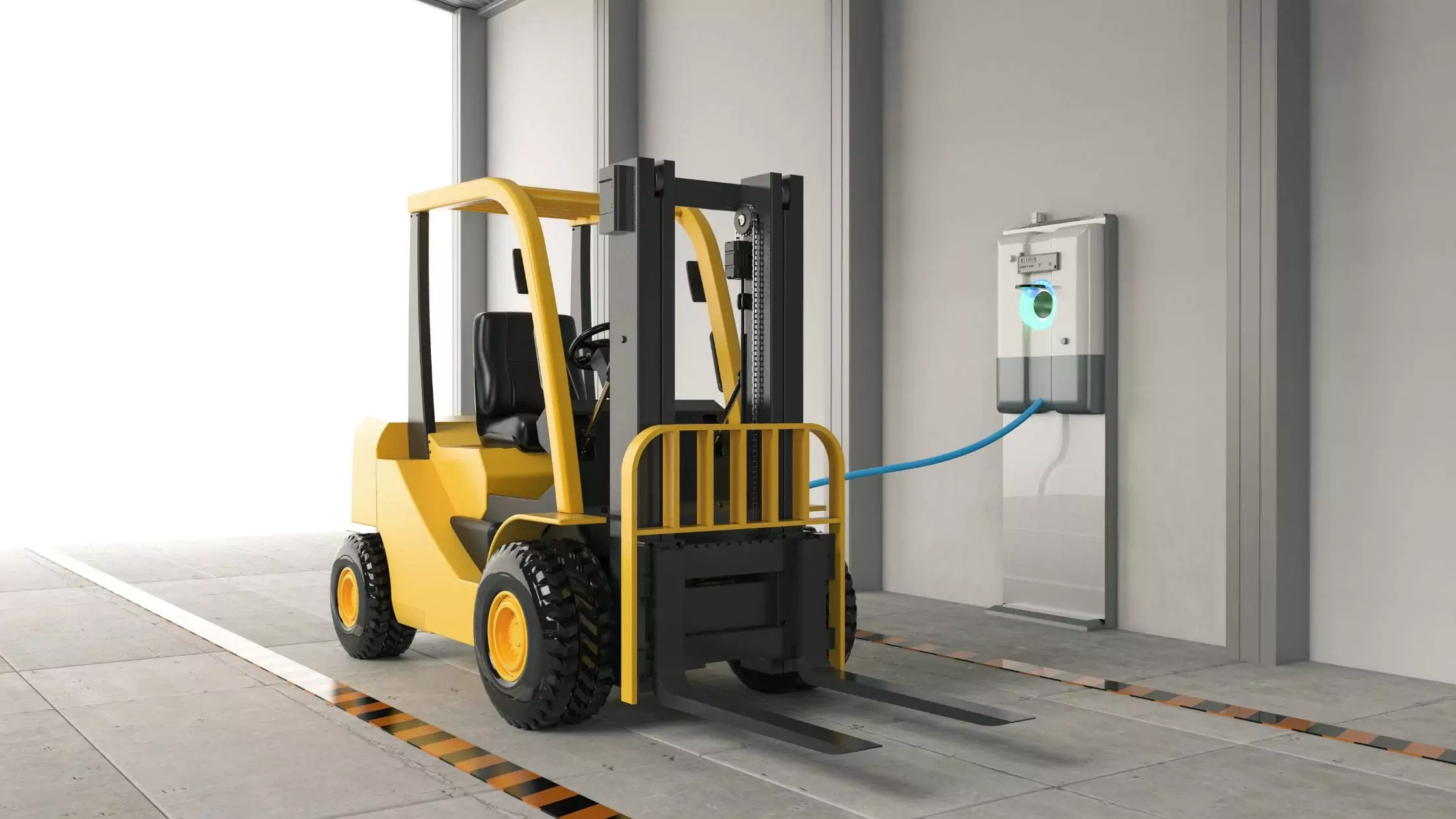

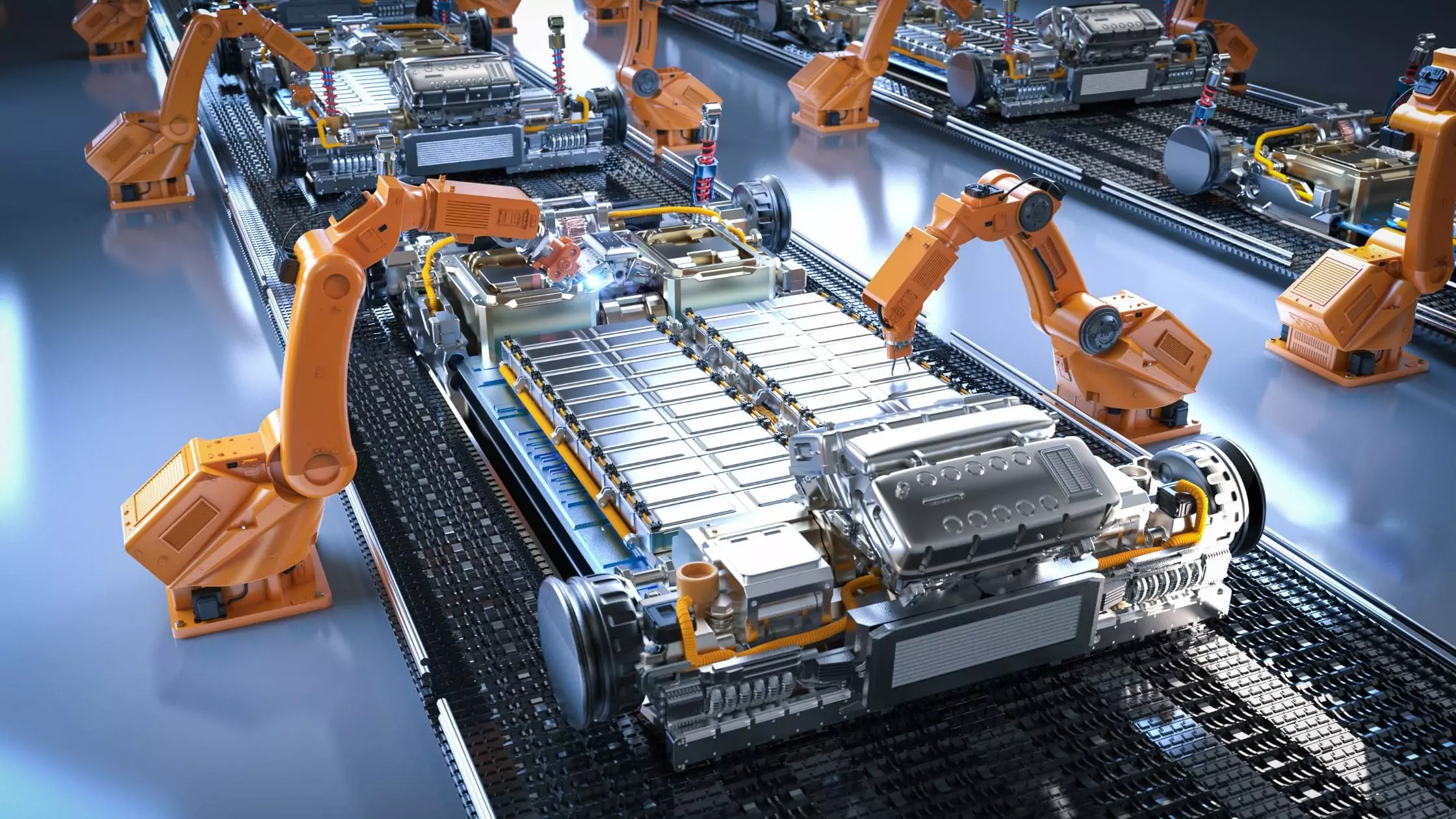
The role of forklift charging in industrial operations cannot be overlooked, and when learning how to charge forklifts, you need to follow the proper process to get best results.
Understanding industrial battery charging is a necessity because it directly impacts the performance and longevity of forklift batteries. According to industry statistics, efficient charging systems can extend battery life by up to 50%, making it essential for businesses to invest in the right charging solutions.
This article focuses on providing you the information needed on how to properly charge forklift batteries and prevent potential hazards.
What Are the Different Forklift Types and Charging Requirements?
Forklifts can be classified into three main types: electric, propane, and diesel. Different types of forklifts have specific charging needs, and understanding these requirements is key to maintaining optimal performance.
Electric Forklifts
Electric forklifts are powered by batteries and are known for their efficiency and lower environmental impact. These forklifts require regular charging, typically done overnight.
Charging an electric forklift battery usually takes about 8-10 hours, followed by a cooling period to ensure safety and efficiency. Electric forklifts are ideal for indoor use and have lower operating costs compared to other types.
In this guide we will focus on different charging methods for electric forklifts and important safety measures to take.
Propane Forklifts
Propane forklifts operate using liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and are known for their efficiency and quick refueling times. Unlike electric forklifts that require battery charging, propane forklifts simply need their fuel tanks replaced or refilled.
This process takes only a few minutes, significantly reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Propane forklifts are versatile and can be used both indoors and outdoors. They are powerful, with quick acceleration and high lifting capacities, making them ideal for heavy-duty material handling. Additionally, they produce fewer emissions compared to diesel forklifts, making them a cleaner option for certain operations.
Diesel Forklifts
Diesel forklifts are renowned for their power and durability, making them suitable for the most demanding industrial applications. These forklifts run on diesel fuel and do not require traditional battery charging. Instead, they need regular refueling, similar to propane forklifts.
Diesel forklifts are particularly effective in outdoor and rough terrain environments due to their robust engine performance. They can handle heavier loads and longer operational hours without compromising efficiency. However, they produce more emissions than electric and propane forklifts, which can be a consideration in certain operational settings.
Regular maintenance and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial to managing the emissions and ensuring optimal performance.
What Are the Components of a Forklift Charging Station?
Three of the main components of a forklift charging station are the charger itself, charging cables and cooling system. A forklift charging station is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of forklift batteries. It is designed to ensure safe and effective battery charging processes.
Below are eight main components of a forklift charging station along with detailed descriptions of each component and its function.
- Charger: The charger converts AC power from the electrical grid into the appropriate DC voltage required for charging the forklift battery. It regulates the current and voltage to ensure that the battery is charged safely and efficiently. Different chargers are available for lead acid batteries, lithium ion batteries, and other types.
- Charging Cables: These cables connect the charger to the battery. They must be in good condition to ensure efficient energy transfer and to prevent safety hazards like electrical shorts or fires. Regular inspection and maintenance of charger cables are crucial for safe operation.
- Ventilation System: Proper ventilation is essential to prevent the buildup of hydrogen gas, which can be produced during the battery charging process. Hydrogen gas is highly flammable, so a good ventilation system ensures that any gas produced is safely dispersed to avoid fire hazards.
- Hydrogen Gas Monitors: These devices detect hydrogen levels in the charging area to prevent gas buildup. They alert personnel if hydrogen levels become unsafe, ensuring timely intervention to prevent accidents.
- Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS monitors and manages the performance of each battery cell. It helps optimize the charge cycles, balance the cells, and prevent issues like overcharging or deep discharging, which can damage the battery.
- Maintenance Log: Keeping a detailed log of all maintenance activities, including battery watering, cleaning, and inspection, helps in tracking the battery’s condition and scheduling preventive maintenance.
- Cooling System: Some charging stations have built-in cooling systems to manage the heat generated during the charging process. This is particularly important for fast charging methods, which produce more heat.
- Battery Equalizer: This device ensures that all cells within the battery are charged to the same voltage, preventing imbalances that can reduce battery life. Equalizing charges are necessary for maintaining battery health, especially for lead acid batteries.
What Are Different Types of Forklift Charging Methods?
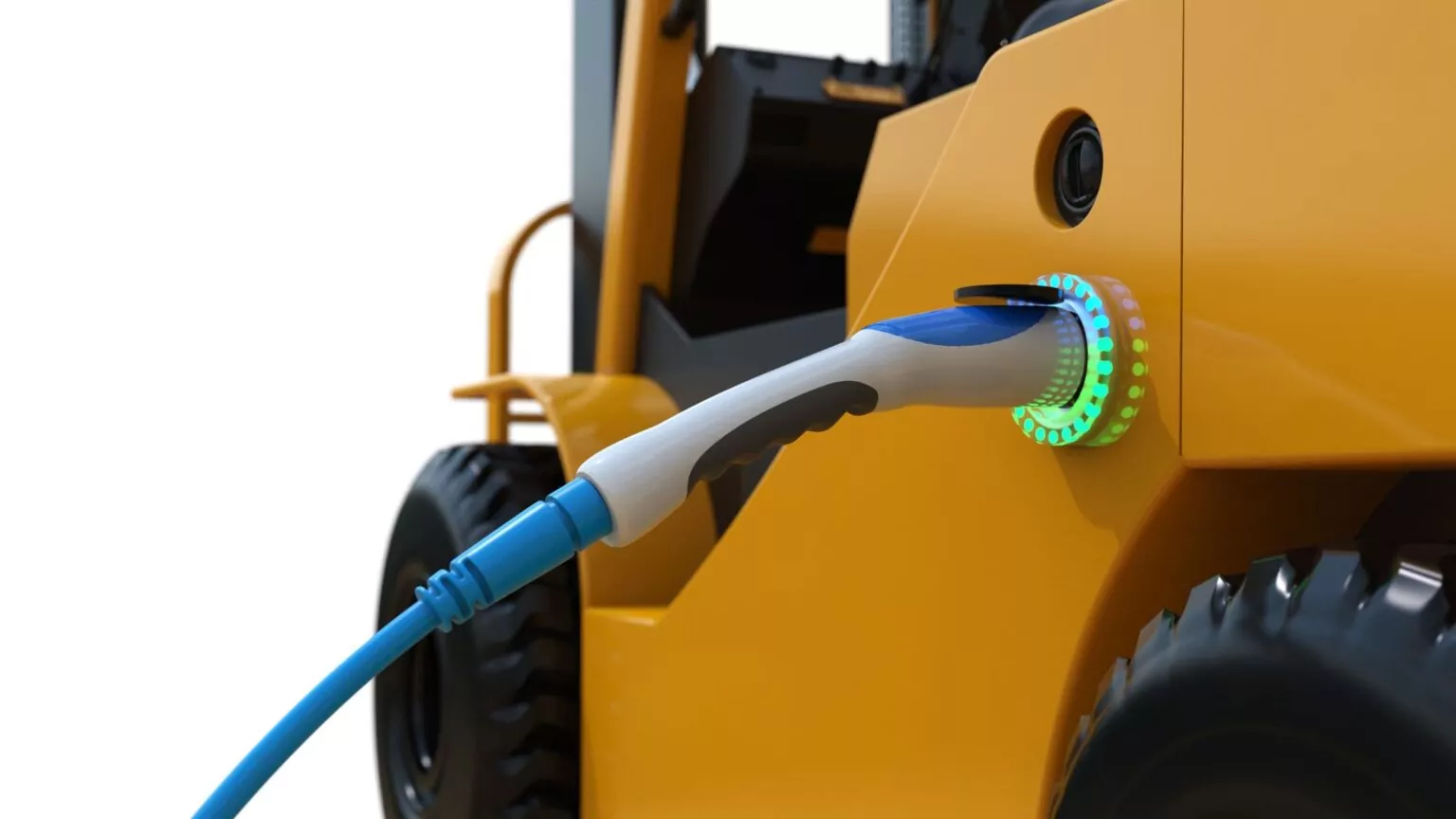

Forklift charging methods vary depending on the operational needs and types of batteries used. The three main charging methods include conventional charging, opportunity charging, and fast charging. Each method has its unique advantages and limitations.
Conventional Charging
Conventional charging is a standard method where a forklift battery is charged overnight with a low current. The process usually takes 8 to 10 hours to reach full charge, followed by 6 to 8 hours of cooling. This method is widely used due to its simplicity and effectiveness in maintaining battery life.
Pros:
- Best for Battery Health: This method is ideal for the battery’s health and longevity, often allowing for the longest battery life, up to 5 years.
- Suitable for Single-Shift Operations: Conventional charging is suitable for operations that run a single shift, as the battery can be charged overnight.
- Lower Initial Cost: The cost of chargers for conventional charging is relatively low, making it an economical option for many businesses.
Cons:
- Long Charging Time: The process takes a long time, which may not be ideal for operations requiring quick turnaround.
- Extended Cooling Time: Requires an additional 6 to 8 hours of cooling after charging, which adds to the overall downtime.
- Not Ideal for Multi-Shift Operations: This method is not suitable for multi-shift operations unless multiple batteries are available for swapping.
- Safety Risks: There is a potential safety risk for employees if battery swapping is needed during shifts.
Opportunity Charging
Opportunity charging is designed to maximize the operational time of forklifts by using high current to quickly charge batteries during short breaks or downtimes. This method allows the battery to be charged incrementally throughout the day, typically bringing it up to 80% charge within 10 to 30 minutes.
Pros:
- Reduces Downtime: By charging during breaks, it keeps forklifts operational for longer periods, significantly reducing downtime.
- Improves Productivity: Eliminates the need for lengthy overnight charges and reduces the necessity for multiple battery sets.
- Ideal for Multi-Shift Operations: Particularly beneficial for operations with multiple shifts, as it ensures forklifts are always ready for use.
- Modern Technology: Advances in technology allow for adjustments in equalization and cooldown times to be managed within an 8-hour period.
Cons:
- Reduces Battery Lifespan: Frequent charging cycles can reduce the overall lifespan of the battery.
- Requires Weekly Equalizing: To reduce sulfation and maintain battery health, weekly equalizing charges are necessary.
- Potential for Overcharging: Requires careful monitoring to prevent overcharging, which can damage the battery.
Fast Charging
Fast charging is a method that uses high current to quickly charge forklift batteries. It allows batteries to reach up to 80% charge within 20 to 30 minutes. This method is ideal for operations requiring continuous use of forklifts with minimal downtime.
It also needs a well-ventilated area to manage the heat generated during the charging process. Fast charging systems are more complex and may require additional training for operators.
Pros:
- Reduces Downtime: Significantly decreases the time needed to charge batteries, keeping forklifts operational.
- Improves Productivity: Eliminates the need for battery swapping and storage areas, thus streamlining operations.
- Ideal for Continuous Use: Perfect for multi-shift operations where forklifts are needed around the clock.
Cons:
- Frequent Equalizing Required: Requires weekly battery equalizing to mitigate sulfation.
- Generates Heat: Produces a lot of heat, which can reduce battery life to about three years compared to five years with conventional charging.
- Higher Wear on Battery: Increases wear and tear, reducing overall battery lifespan.
Conventional Plug-In Charging
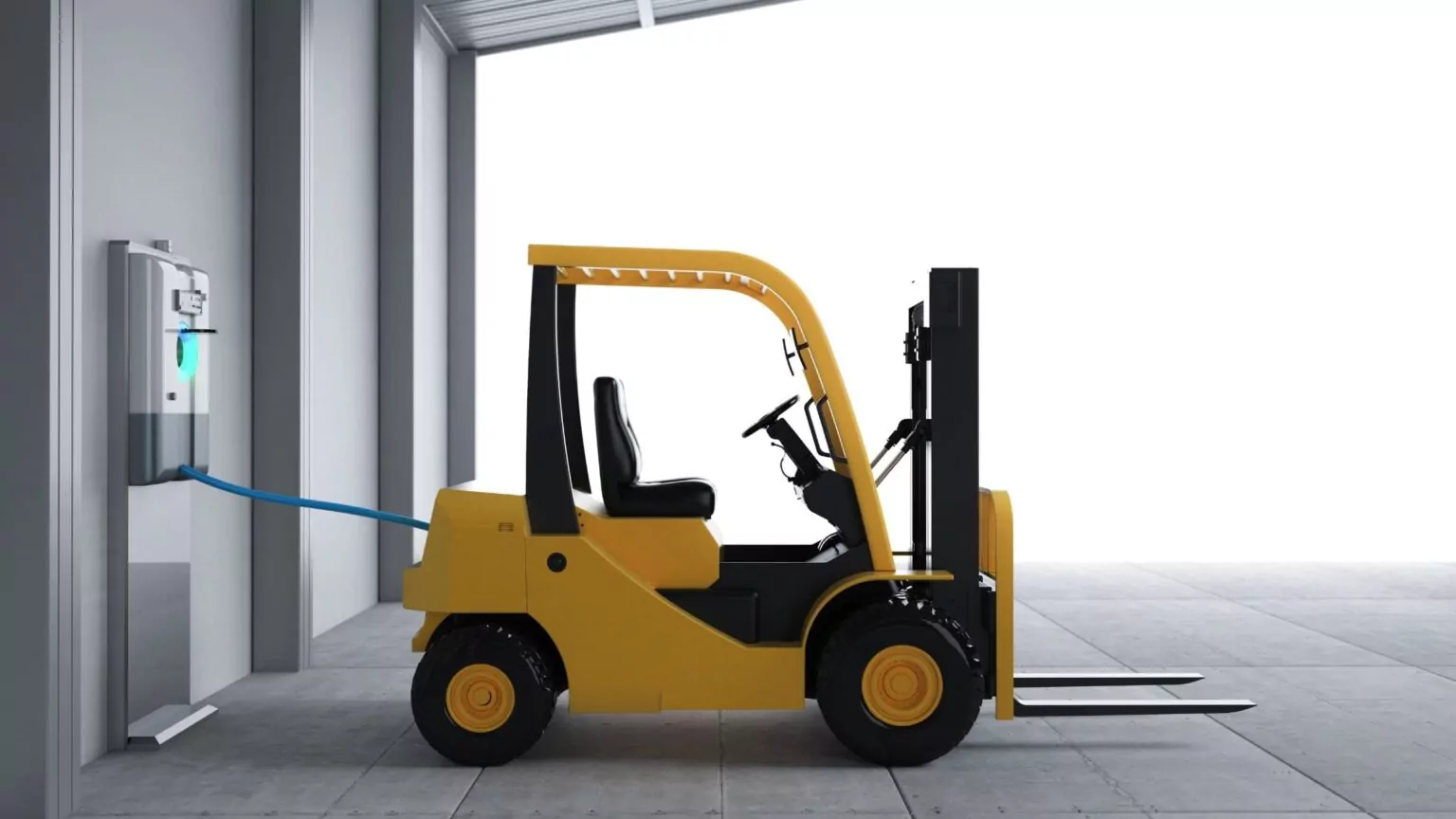

Also known as wired charging, conventional plug-in charging involves manually connecting the forklift to a power source using a cable. This method can be fast, especially with wired fast charging, but it requires strict adherence to safety procedures.
Pros:
- Lower Cost for Charger: The initial cost for the charger is lower compared to other methods.
- Fast Charging Possible: Can be fast, particularly with wired fast charging setups.
Cons:
- High Labor Costs: Requires proper charge procedures, which can be labor-intensive.
- Maintenance Costs: High maintenance costs due to broken chargers, connectors, and cables.
- Safety Risks: Increased safety risks and reliance on operators for safe operation.
- Dedicated Charging Area: Requires a dedicated charging area, making it less flexible.
- Not Suitable for Continuous Heavy Usage: Best for operations that do not require constant forklift usage.
Forklift Battery Swapping
Battery swapping is a method where a forklift’s depleted battery is replaced with a fully charged one. This method uses specialized equipment such as battery hoists or automated systems for removing and installing batteries.
Pros:
- No Electrical Upgrades Needed: Unlike wired charging, battery swapping does not require significant electrical upgrades.
- Reliable: Can be more dependable than wired charging methods, reducing the risk of downtime.
Cons:
- High Upfront Cost: Requires significant investment in additional battery inventory and specialized equipment.
- Labor-Intensive: The process is time-consuming and demands manual labor.
- Safety Risks: Increased risk of dropped batteries and spills, posing safety hazards.
- Dedicated Space: Needs a dedicated space for battery swapping.
Wireless Forklift Charging
Wireless forklift charging involves transferring electrical energy from a wireless charging station (transmitter) to a receiving unit (receiver) mounted on the forklift. This is done using inductive or conductive technology.
Pros:
- Automatic Charging: Starts and stops charging automatically, reducing manual labor.
- Safety: No exposed connectors or cables, enhancing safety.
- Real Estate Utilization: Eliminates the need for large charging stations, optimizing space.
- Easy Installation: Simplifies installation and reduces operating costs.
- Energy Efficiency: Improves energy efficiency and provides flexibility in charging locations.
Cons:
- Energy Efficiency Variability: Energy efficiency can be slightly lower depending on the alignment of the transmitter and receiver.
- Alignment Challenges: Potential issues with alignment and technology compatibility.
Solar Battery Charging
Solar battery charging uses solar panels to generate electricity, which is then used to charge forklift batteries. This method harnesses renewable energy from the sun, converting it into electricity that is stored in a battery bank.
Pros:
- Renewable Energy Source: Reduces energy costs by using sunlight.
- Environmentally Friendly: Generates clean energy, reducing carbon footprint.
- Suitable for Remote Locations: Ideal for areas without reliable grid access.
Cons:
- High Initial Setup Cost: Significant investment in solar panels and related infrastructure.
- Dependence on Sunlight: Requires a backup charging method for cloudy days or nighttime.
- Maintenance Needs: Regular maintenance of solar panels and infrastructure.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cells generate electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen, providing a quick refueling alternative for forklifts. This process produces electricity through electrolysis, and the hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks on the forklift.
Pros:
- Zero Emissions: Produces only water vapor, making it environmentally friendly.
- Reduced Electricity Costs: Eliminates the need for electrical charging.
- Suitable for Outdoor Operations: Can be used in various environments without dependency on the grid.
Cons:
- High Upfront Costs: Significant initial investment in hydrogen refueling infrastructure.
- Ongoing Costs: Continual costs for hydrogen production and refueling.
- Manual Refueling: Similar to conventional gas or diesel forklifts, requiring manual labor.
When to Charge a Forklift Battery?
Charge your forklift battery when it reaches 20% to 30% discharge. This range, known as the “red zone,” is critical to prevent damage to the battery. Allowing the battery to discharge below 20% can lead to several issues:
- Sulfation Build-Up in lead-acid batteries: Sulfation occurs when sulfuric acid in the electrolyte attaches to the battery plates during discharge. This build-up reduces the battery’s efficiency and lifespan.
- Battery Overheating: Discharged batteries can overheat, leading to potential failures and safety hazards.
- Stratification: Uneven acid distribution within the battery can decrease its performance.
Letting a forklift battery discharge too deeply can cause significant problems. Among these, sulfation is the most common and noticeable. Sulfation happens when:
- The battery hasn’t been fully charged in a while.
- The water level is too low, making the electrolyte too concentrated.
- The battery remains in a depleted state for too long.
To avoid sulfation and its detrimental effects, proper forklift battery charging is essential. Charging reverses the sulfation process by driving the sulfate from the plates back into the electrolyte acid. Here are key steps to ensure effective charging:
- Regular Charging: Stick to a consistent charging schedule to prevent deep discharge.
- Maintenance: Monitor and maintain water levels and electrolyte concentration.
- Safety Procedures: Follow proper forklift battery charging procedures to ensure safety and efficiency.
How to Charge a Forklift Battery: Step-by-Step List

Here are the eleven important steps to follow when charging a forklift battery
Establish a Safe Charging Station
- Location: Designate a well-ventilated area for charging to avoid hydrogen gas buildup and ensure safety. Poor ventilation can lead to dangerous hydrogen gas accumulation.
- Safety Equipment: Equip the station with a fire extinguisher, acid neutralization materials, acid-resistant floors, an eyewash station, and a safety shower. This equipment is crucial for handling potential acid spills and fire hazards.
- Signage: Install no-smoking signs to prevent fire hazards. Hydrogen gas is highly flammable, and smoking should be strictly prohibited in charging areas.
Prepare the Forklift
- Parking: Park the forklift in the designated charging area, set the parking brake, and turn off the ignition. This ensures the forklift is stable and prevents accidental movement during charging.
- Hood: Raise the forklift’s hood for heat dispersion and ventilation. Proper ventilation helps prevent overheating of the battery during charging.
Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- PPE Requirements: Wear face shields, safety glasses, rubber gloves, and a protective apron to protect against acid splashes and electrical hazards. PPE minimizes the risk of injuries from acid and electrical shocks.
- Remove Jewelry: To reduce the risk of electrocution, remove any metal jewelry before starting the charging process. Metal can conduct electricity and cause severe shocks.
Inspect the Battery and Charger
- Voltage and Amps Matching: Ensure the charger’s output voltage and ampere-hour (AH) rating match the battery’s specifications. Incorrect matching can damage the battery or the charger.
- Condition Check: Inspect charger cables and connectors for damage such as burns, cracks, or frayed wires. Repair any damages before proceeding to avoid electrical hazards.
- Battery Temperature: Confirm the battery is not too hot or cold before charging. Charging at extreme temperatures can damage the battery and reduce its efficiency.
Disconnect the Battery from the Forklift
- Exposure: Lift the seat to expose the battery. This allows easy access to the battery for inspection and charging.
- Disconnecting: Safely disconnect the battery cable from the forklift to avoid damage. Ensure the connectors are clean and undamaged.
- Transport Precautions: If removing the battery, use appropriate equipment like a pallet jack with a transfer carriage and ensure the battery is securely transported. Batteries are heavy and can be dangerous to move manually.
Connect the Battery to the Charger
- Proper Connection: Connect the charger to the battery connector, not the forklift terminal. Incorrect connections can lead to charging failures and equipment damage.
- Activation: The charger should turn on automatically, or manually start it if necessary. Ensure the charger indicates that charging is in progress.
Charging Methods and Duration
- Conventional Charging: Takes about 8 hours for charging and an additional 8 hours for cooling. Best for single-shift operations where the battery can charge overnight.
- Opportunity Charging: Takes 10-30 minutes to charge up to 80%. Suitable for two-shift operations but can reduce battery lifespan if used frequently.
- Fast Charging: Also takes 10-30 minutes for 80% charge. Suitable for three-shift operations but is hard on the battery and requires weekly equalizing charges to maintain battery health.
Monitor the Charging Process
- Check Progress: Ensure the charger is indicating active charging. Monitor the battery temperature and charger status to prevent overheating.
- Safety: Never interrupt the charging process unless absolutely necessary. Always stop the charger before disconnecting to prevent electrical arcing.
Complete the Charging Cycle
- Full Charge: Wait until the battery is 100% charged. The charger may stop automatically, or press the “Stop” button if it requires manual termination. A full charge ensures the battery’s acid is properly balanced.
- Cooling Time: Allow the battery to cool down after charging. This step is important to prevent thermal damage to the battery.
Disconnect the Charger and Reconnect the Battery
- Safety First: Turn off the charger before disconnecting to avoid electrical hazards. Ensure all connections are properly terminated to prevent accidents.
- Reconnect: Plug the battery connector back into the forklift connector. Ensure the connection is secure and free from corrosion.
Maintenance Post-Charging
- Watering the Battery: For lead-acid batteries, check and maintain proper water levels after the battery has cooled. Only add water if needed, avoiding over- or underwatering. Use distilled water to avoid mineral build-up.
- Watering Log: Keep a detailed log of watering times and amounts to ensure proper maintenance and facilitate warranty claims if necessary. Accurate records help track battery health and maintenance schedules.
How Long Does It Take to Charge a Forklift Battery?

The time required to charge a forklift battery varies depending on the type of battery and charger you use.
Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries
For a flooded lead-acid battery, you should let it run down to the red zone, which is about 20% to 30% discharge, before charging it back to 100%. This process typically takes about eight hours to fully charge the battery. Following the “8-8-8 Rule” is recommended for optimal utilization:
- 8 hours in operation
- 8 hours on the charger
- 8 hours to cool down
These batteries require a substantial cooling period after charging to maintain their health and longevity. While conventional charging suits single-shift operations, using these batteries for opportunity or rapid charging involves charging them during all scheduled breaks over 15 minutes. This method requires specific batteries and chargers designed for frequent short charging sessions to avoid damaging the battery.
Thin Plate Pure Lead (TPPL) Batteries
TPPL batteries benefit from opportunity charging, meaning you charge them whenever convenient, such as during lunch breaks. These batteries perform best and have a longer lifespan when kept at the highest charge possible. The general rule is: “if the truck sits longer than 15 minutes, plug it in.” TPPL batteries usually only need to be fully charged once a week.
They do not require watering and have low internal resistance, allowing for fast and frequent charging without overheating. This makes them highly efficient and popular in modern material handling operations.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries offer the fastest recharge capabilities, often reaching a full charge from 0% to 100% within an hour using high-frequency battery chargers. Quality lithium-ion batteries, typically made from nickel manganese cobalt, are known for their reliability and safety. They are UL-approved, ensuring they meet safety standards. Lithium batteries are suitable for operations requiring quick turnarounds and minimal downtime.
- Opportunity Charging: Suitable for TPPL and some lead-acid batteries, this method involves charging during short breaks to keep the battery at a high charge level. It’s essential to use batteries and chargers specifically designed for this purpose to prevent damage.
- Rapid Charging: Often used with lithium-ion batteries, this method allows for quick charging times but requires high-quality chargers and batteries to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Conventional Charging: Ideal for flooded lead-acid batteries, this method involves a full charge cycle followed by a cooling period, best for operations that can accommodate longer charging times.
How Long Does a Forklift Run After Charging?

The runtime of a forklift after charging varies based on the type of battery and its maintenance. Here are some details:
- Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries: Flooded lead-acid batteries typically operate for 8 hours on a full charge. These batteries require 8 hours to charge fully and another 8 hours to cool down, making overnight charging ideal if the forklift is only used during the day. Maintaining clean batteries and following proper charging protocols can help maximize their runtime.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Lithium-ion batteries can also last up to 8 hours on a single charge. Unlike lead-acid batteries, they do not require a cool-down period between charging and operating. High-quality lithium-ion batteries can be rapidly charged, reaching full capacity in about an hour. These batteries are designed to handle frequent and fast charging without overheating.
What Are the Safety Practices for Charging a Forklift and Potential Hazards?
Charging a forklift battery involves several safety practices to prevent hazards. Here are ten key guidelines to follow:
- Be Careful When Moving Forklift Batteries: Lead acid batteries are extremely heavy and often cannot be moved without mechanical assistance. Use proper equipment like pallet jacks to facilitate easy movement and avoid manual lifting. This helps prevent injuries from awkward body movements and improper lifting techniques.
- Avoid Crush and Caught-Between Injuries: When moving batteries, ensure that the equipment used has fail-safes or guards to prevent batteries from falling or moving uncontrollably. Employees should wear steel-toed work shoes and follow procedures to stay out of the battery’s path, minimizing the risk of crush and caught-between injuries.
- Ventilate Charging Areas to Prevent Flammable Gas: Charging batteries generate hydrogen gas, which is highly flammable. Ensure the charging area is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of hydrogen gas, which can pose an explosion hazard. Use hydrogen gas monitors and keep the area free of open flames and spark-producing devices.
- Protect Yourself from Corrosive Electrolytes: The electrolyte in batteries contains sulfuric acid, which is corrosive and can cause severe chemical burns. Always wear face shields, splash goggles, gloves, and aprons to protect against splashes. Eyewash stations or drench showers should be available to quickly neutralize any acid exposure.
- Handle Spilled Electrolyte with Care : Spilled electrolyte is both a chemical burn hazard and a slip hazard. Keep spill kits in battery rooms and charging areas for quick response. Employees should know how to use personal protective equipment (PPE) and neutralizers to handle spills effectively.
- Be Aware of Electrical Charges in Batteries: Lead acid batteries hold an electrical charge and can potentially arc. Charge batteries when they reach about 30% capacity using cables in good condition. Employees should remove metal jewelry to avoid electrical shocks and be cautious of other metals that could increase explosion risk.
- Use Proper Equipment to Lift Forklift Batteries: Forklift batteries can weigh up to 3,000 lbs. Never attempt to lift a forklift battery manually. Use equipment like a pallet jack equipped with a transfer carriage to handle the heavy weight safely.
- Turn Off and Avoid Using Smoking Batteries: If a battery starts smoking, turn it off immediately and do not use it again. Smoke indicates a serious malfunction that could lead to fire or explosion, requiring the battery to be handled by professionals.
- Always Wear Protective Gear : Always follow OSHA recommendations for protective gear. Batteries contain sulfuric acid, which can cause severe burns. Remove all metallic jewelry when handling and charging batteries to minimize the risk of electric shock and acid burns.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation in charging areas to prevent the buildup of hydrogen gas. This is especially important for lead acid batteries, which emit hydrogen during charging. Proper ventilation reduces the risk of explosion and maintains a safe working environment.
Whata are Potential Hazards when Charging a Forklift Battery?
There are five main hazards you should understand to keep a safe charging environment:
- Crush and Caught-Between Injuries: Use mechanical assistance to move heavy batteries and wear steel-toed shoes to avoid injuries.
- Flammable Gas: Ensure proper ventilation to prevent hydrogen gas buildup and use hydrogen gas monitors.
- Corrosive Electrolytes: Wear protective gear and have eyewash stations available to handle sulfuric acid spills.
- Spilled Electrolyte: Keep spill kits handy to quickly neutralize and clean up spills to prevent burns and slips.
- Electrical Charge: Handle batteries carefully to avoid electrical arcing and remove metal jewelry before charging.
Should You Charge a Dead Forklift Battery?
No, you should not charge a dead forklift battery. For a flooded lead-acid battery, you never want to let it run down to 0% charge. As these batteries discharge, lead sulfate crystals form on the plates. This buildup creates an electrically resistant surface, depleting the battery’s ability to charge and potentially making it unusable. To avoid this, follow proper charging protocols and start charging when the battery is in the “red zone” (20% to 30% charge). Charging at this point provides the best balance of battery life, performance, and downtime. Always ensure the battery is fully charged before removing it from the charger.
Maintenance Tips for Forklift Batteries
Proper maintenance of your forklift batteries is essential to ensure their longevity and reliability. Here are eight practical tips to keep your forklift batteries in top condition:
- Follow Manufacturer’s Charge Cycle Recommendations: Always adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended charge cycles. Exceeding these can shorten the battery’s lifespan. Efficient charging ensures longer battery life.
- Equalize the Battery Regularly: Equalizing the battery involves overcharging it periodically to remove any sulfate buildup. This should be done according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, which depend on the charging method used.
- Charge the Battery Correctly: Avoid undercharging or overcharging the battery. Always charge at the appropriate discharge level (20% to 30%) to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance.
- Don’t Wait for Low Battery Signs: Charge the battery when it reaches 20% to 30% charge. Waiting until the battery shows signs like slow starts or dim headlights can lead to breakdowns and reduce battery life.
- Check the Battery’s Water Level: Add deionized or distilled water every five to ten charges, as recommended by the manufacturer. Only add water after charging to avoid overfilling and crystal formation on the lead plates.
- Clean Batteries Every Month: Clean the top of each battery monthly using battery cleaner or warm water. This prevents chemical buildup, which can lead to tray corrosion and may void the manufacturer’s warranty.
- Inspect for Damage and Wear: Regularly inspect the battery for any signs of damage or wear, including cracks or leaks. Address any issues immediately to avoid further damage and ensure safe operation.
- Maintain Proper Charging Area Conditions: Ensure the charging area is clean, well-ventilated, and equipped with necessary safety equipment like fire extinguishers and eyewash stations. This helps prevent accidents and prolongs battery life.
How Often Should Forklift Batteries Be Replaced?
Forklift batteries have a typical lifespan that varies from five to ten years based on usage, maintenance, and chemistry. Here’s what you need to know:
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid forklift batteries usually last about five years, assuming they go through one charge cycle per day. This equates to roughly 1,500 charge cycles. Signs that indicate the need for replacement include:
- Decreased Runtime: If the battery no longer holds a charge as long as it used to, it may be nearing the end of its life.
- Difficulty Holding Charge: If the battery discharges quickly after being fully charged, it’s a sign of deterioration.
- Visible Damage: Cracks, leaks, or bulging in the battery casing are clear indicators that it needs to be replaced.
- Increased Maintenance Issues: Frequent issues with maintaining water levels or more frequent sulfation build-up suggest the battery is aging.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries generally have a longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries, often lasting up to ten years or more. These batteries require minimal maintenance and have a higher tolerance for frequent charging. Signs that a lithium-ion battery needs replacement include:
- Reduced Efficiency: Longer charging times and shorter operational periods can indicate battery wear.
- Inconsistent Performance: Fluctuations in performance or the battery not reaching full charge are signs of aging.
- Overheating: If the battery frequently overheats, it may be nearing the end of its useful life.
How to Choose the Right Forklift Charging System?
Choosing the right forklift charging system is crucial for maximizing efficiency and minimizing downtime in your operations. Here are ten practical tips to help you select the most appropriate system based on your specific needs:
Assess Operation Size
When selecting a forklift charging system, the size of your operation plays a significant role. Furthermore, remember that no matter the operation most of the times you will need an industrial battery charger. For smaller operations with fewer forklifts, conventional charging methods might suffice. This approach is cost-effective and meets the needs without requiring complex infrastructure. Conversely, larger operations, especially those running multiple shifts, may benefit from opportunity or fast charging systems. These systems help minimize downtime and ensure forklifts remain operational throughout the day.
Assess Battery Voltage and Type
It’s crucial to match your charging system to the specific type and voltage of your forklift batteries. For operations using lead acid batteries, ensure the charging system aligns with the voltage and amp-hour rating of these batteries. Lead acid batteries are common and reliable, but they have specific charging requirements. If your operation uses lithium-ion batteries, choose a charger designed for this battery chemistry. Lithium-ion batteries require different protocols than lead acid ones, including distinct voltage and current specifications.
Assess Charging Time Needs
The required charging time significantly impacts your choice of a charging system. Conventional charging methods are ideal for single-shift operations, typically taking about 8 hours to fully charge a forklift battery. This method fits well with overnight charging when the forklifts are not in use. On the other hand, fast charging is more suitable for multi-shift operations. Fast chargers can recharge a forklift battery in 30 minutes to an hour, drastically reducing downtime and ensuring forklifts are ready to use at all times.
Assess Electrical Setup and Infrastructure
Your current electrical infrastructure must support the power demands of your chosen charging system. Fast and opportunity chargers often require upgrades to your electrical setup. Evaluate whether your existing infrastructure can handle the power requirements, and plan for necessary electrical upgrades, including proper ventilation to manage hydrogen gas generated when charging lead acid batteries.
Assess Frequency of Use
The frequency of forklift use in your operation dictates the type of charging system needed. For operations where forklifts are used continuously, opportunity charging systems are beneficial. These systems allow for partial charges during breaks, keeping the batteries topped off without significant downtime. For moderate use operations, conventional charging is appropriate, aligning with the 8-8-8 rule: 8 hours of use, 8 hours of charging, and 8 hours of cooling.
Assess Budget
Consider both the initial and ongoing costs when selecting a charging system. Fast charging and lithium-ion systems have higher upfront costs but may prove cost-effective over time due to reduced downtime and extended battery life. Lead acid batteries, while cheaper initially, require regular maintenance, such as watering, which can increase long-term costs. Assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement expenses.
Assess Compatibility with Current Equipment
Ensure that the charging system you choose is compatible with your existing forklift batteries. This compatibility avoids additional costs for new batteries or chargers. Match the chargers with your battery type and voltage to prevent damage and ensure efficient charging. Incompatibility can lead to inefficiencies and potential damage to your equipment.
Assess Safety Measure and Features
Safety is paramount in forklift battery charging areas. Proper ventilation is essential, especially when charging lead acid batteries, to prevent hydrogen gas buildup. Equip charging stations with safety features like fire extinguishers, eyewash stations, and personal protective equipment (PPE) to handle potential hazards. Adopting these safety measures helps mitigate risks associated with battery charging.
TL power is one of the leading manufacturers of forklift battery chargers. Every battery charging station comes with safety features like burnout protection, short circuit protection, hardware and voltage and current self-test protection and automatic shutoff when batteries are fully charged. Tl Power industrial battery chargers have proven verification in all kinds of tough industrial environments like wet, hot, high vibration, dust and debris.
Assess Manufacturer Guidelines
Follow the guidelines provided by the battery and charger manufacturers regarding charge cycles, equalization, and maintenance. Adhering to these recommendations ensures you maximize battery life and performance. Additionally, ensure that the chosen charging system does not void any warranties on your forklift batteries. Manufacturer guidelines often include important details that can affect warranty coverage.
Assess for Future Expansion
Consider the scalability of your charging system. Choose a system that can grow with your operation. If you plan to expand or add more forklifts, ensure your charging system can accommodate this increased demand. Stay informed about advancements in charging technology, as newer solutions might offer more efficient or cost-effective options in the future. This forward-thinking approach helps in maintaining operational efficiency as your needs evolve.
Match the Battery Amp Hours to the Charger Amp Hours

Matching the battery’s amp-hour (AH) rating to the charger’s output is essential for efficient and safe charging. Here are some practical tips:
- Identify Battery AH Rating: Check the battery’s AH rating, usually found on the battery’s data plate. This rating indicates how much energy the battery can store.
- Charger Compatibility: Ensure the charger’s output matches the battery’s AH rating. Using a charger with a higher or lower AH output than required can lead to inefficient charging or potential damage.
- Charging Time Consideration: If your operation requires quick turnaround times, consider chargers that can handle higher AH ratings to reduce charging time.
- Efficiency: Matching the charger’s AH rating to the battery ensures optimal charging efficiency, which helps extend the battery’s lifespan.
- Safety: Correctly matching the AH ratings minimizes the risk of overheating and reduces wear on both the charger and the battery.
- Multiple Batteries: If you use multiple batteries with different AH ratings, consider using a charger with adjustable settings to accommodate various battery sizes.
- Consult Manufacturer Recommendations: Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for both the battery and charger to ensure compatibility and safety.
- Regular Checks: Periodically verify that the charger and battery AH ratings remain compatible, especially if there are changes in your battery inventory.
- Load Balancing: For operations with heavy usage, using a charger with the correct AH rating helps balance the load across multiple batteries, preventing overuse of a single unit.
- Technological Upgrades: Consider chargers with smart technology that can automatically adjust to the battery’s AH rating, providing precise and efficient charging.
Choose the Correct Output Voltage
Selecting the correct output voltage for your forklift battery charger is crucial for maintaining battery health and ensuring efficient operations. Here’s how to do it:
- Check Battery Voltage: Identify the voltage requirement of your forklift batteries. Common forklift battery voltages include 24V, 36V, 48V, and higher.
- Charger Voltage Match: Ensure the charger’s output voltage matches the battery’s voltage. Using the incorrect voltage can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan.
- Consider Voltage Variability: Some chargers offer adjustable voltage settings to accommodate different battery voltages. This flexibility can be useful if you have a diverse fleet of forklifts.
- Voltage Compatibility: Confirm that the charger’s voltage output is compatible with the battery’s chemistry, whether it’s lead acid or lithium-ion.
- Operational Efficiency: Matching the voltage correctly ensures efficient energy transfer, reducing charging times and energy consumption.
- Safety Measures: Using the correct voltage helps prevent overheating and electrical faults, enhancing safety during the charging process.
- Manufacturer Specifications: Always refer to the battery and charger manufacturer’s specifications to ensure you are using the correct voltage.
- Multi-Voltage Chargers: For operations with mixed battery voltages, consider investing in multi-voltage chargers that can automatically adjust to the required output.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor the charger’s output voltage and ensure it remains consistent with the battery’s needs. This helps maintain optimal battery performance.
- Future-Proofing: Consider future expansions of your forklift fleet. Selecting chargers with flexible voltage outputs can accommodate new battery types and voltages, ensuring long-term utility.
Choose the Correct Input Voltage
Selecting the correct input voltage for your forklift charging system ensures that the charger operates efficiently and safely. Here’s how you can do it:
- Identify Power Supply Voltage: Determine the voltage of your facility’s power supply. This information is crucial to ensure compatibility with the charger.
- Check Battery Requirements: Verify the voltage requirements of your forklift batteries. This is usually indicated on the battery’s data plate.
- Match Voltage: Ensure that the charger’s input voltage matches the power supply voltage to avoid electrical issues.
- Voltage Range: Some chargers can operate within a range of input voltages. Check if your charger has this capability for flexibility.
- Stable Power Source: Ensure the power source is stable and does not fluctuate. Unstable power can damage both the charger and the battery.
- Facility Infrastructure: Assess if your facility’s electrical infrastructure can support the charger’s voltage requirements. Upgrading the infrastructure might be necessary.
- Consult an Electrician: If unsure about the voltage compatibility, consult a licensed electrician to avoid any potential hazards.
- Backup Power: Consider having a backup power source for the charging system to maintain operations during power outages.
- Energy Efficiency: Opt for energy-efficient chargers that minimize electricity consumption, reducing operational costs.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure the charging system complies with local electrical codes and safety regulations.
Choose the Correct Input Phase
The input phase of your charger needs to match the power supply to ensure efficient and safe operation. Follow these tips to choose the correct input phase:
- Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Power: Determine whether your facility uses single-phase or three-phase power. This is critical for selecting the correct charger.
- Charger Specifications: Check the charger’s specifications to see if it supports single-phase or three-phase input.
- Power Availability: Verify the availability of the required phase in your facility. Installing a three-phase charger in a single-phase facility is not feasible without modifications.
- Operational Requirements: Consider the power needs of your operations. Three-phase power is generally more efficient and suitable for larger operations.
- Installation Costs: Installing a three-phase system might involve higher initial costs, but it can lead to long-term savings due to better efficiency.
- Electrical Load: Ensure that the electrical load of the charger does not exceed the capacity of your facility’s power supply.
- Maintenance: Three-phase systems typically require less maintenance and provide smoother operation compared to single-phase systems.
- Compatibility: Confirm that all components of your charging system are compatible with the selected phase to prevent damage.
- Expert Advice: Consult with an electrical engineer to ensure that the chosen phase is suitable for your specific needs.
- Scalability: Choose a system that can scale with your operations. If you plan to expand, a three-phase system might offer better scalability.
Choose a Charger With an Equalize Setting
An equalize setting on a charger helps maintain the health of lead-acid batteries by preventing sulfate build-up. Here’s how to select a charger with this feature:
- Understand Equalization: Equalization involves overcharging the battery at a controlled rate to remove sulfate crystals and balance the cell voltage.
- Charger Compatibility: Ensure the charger is compatible with the type of batteries you are using, especially lead-acid batteries.
- Automatic Equalization: Opt for chargers that offer automatic equalization settings to simplify the process.
- Manual Equalization Option: Some chargers allow manual equalization, giving you control over when to perform this maintenance task.
- Frequency of Equalization: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for how often to equalize the batteries to maintain optimal battery health.
- Monitoring Capabilities: Choose a charger that can monitor and display the equalization process, ensuring that it is performed correctly.
- Prevent Over-Equalization: Ensure the charger has safeguards to prevent over-equalization, which can damage the battery.
- Energy Efficiency: Select chargers that perform equalization efficiently, minimizing energy consumption.
- Maintenance Logs: Keep a log of equalization cycles to track battery health and ensure consistent maintenance.
- Manufacturer Support: Choose a charger from a reputable manufacturer that offers support and guidance on equalization settings.
How Much Does It Cost to Charge a Forklift?
The cost of charging a forklift can vary based on several factors, including the type of battery, the charging method, and local electricity rates. Here’s a detailed look at how to calculate these costs:
- Identify Electricity Rate: Find out the cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh) from your electricity bill. Rates can vary but typically range from $0.10 to $0.20 per kWh in the US.
- Determine Battery Capacity: Identify the amp-hour (Ah) rating of your forklift battery. This information is usually on the battery’s data plate.
- Calculate kWh Required: To find out how many kWh are needed to charge the battery, use the formula: kWh = (Battery Voltage x Amp-Hours) / 1000. For a 48-volt battery with a 400 Ah rating, the calculation would be (48 x 400) / 1000 = 19.2 kWh.
- Charging Efficiency: Consider the efficiency of the charger, which is typically around 85%. Adjust the required kWh to account for this by dividing the total kWh by the efficiency. 19.2 kWh / 0.85 = 22.6 kWh.
- Calculate Cost: Multiply the adjusted kWh by your electricity rate. Example: 22.6 kWh x $0.15 per kWh = $3.39.
- Typical Charging Times: Lead acid batteries typically take 8 hours to charge fully while lithium-Ion batteries can charge in about 1 to 2 hours, depending on the charger.
What Are the OSHA Requirements for Forklift Battery Charging?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has specific requirements to ensure safety during forklift battery charging. Here are the key guidelines and precautions:
- Designated Charging Areas: OSHA requires that forklift battery charging areas be clearly designated and marked. These areas should be well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of hydrogen gas, which can be explosive.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in the charging area to disperse hydrogen gas produced during battery charging. Hydrogen gas monitors may be required to detect dangerous levels.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers must use PPE, including face shields, safety glasses, rubber gloves, and aprons, to protect against acid splashes and electrical hazards.
- No Smoking: Smoking is strictly prohibited in battery charging areas due to the risk of hydrogen gas explosions. Clear signage should be posted to enforce this rule.
- Fire Protection: Install fire extinguishers in the charging area. Ensure that workers are trained on how to use them and know the locations of all fire safety equipment.
- Spill Kits: Keep spill kits in the charging area to quickly address any acid spills. Workers should be trained on how to use these kits effectively.
- Eyewash Stations: Eyewash stations or safety showers must be readily accessible in case of acid splashes. Ensure these stations are functional and regularly maintained.
- Battery Handling Equipment: Use appropriate equipment, such as pallet jacks or transfer carriages, to move heavy batteries. Avoid manual lifting to prevent injuries.
- Charger Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain battery chargers and cables to ensure they are in good working condition. Damaged equipment should be repaired or replaced immediately.
- Training: Provide comprehensive training for workers on the proper procedures for battery charging, including safety protocols and emergency response actions.
Conclusion
To properly charge a forklift battery isn’t a complicated procedure, as following the recommended charging cycles and methods will keep your battery in the best state. It’s also important that you adhere to the OSHA guidelines, because not only does it put you in good legal standing, it also ensures the safety of your workforce, and further extends the lifespan of your battery.
Knowing when to change a forklift battery is just as important as maintaining it, because a damaged forklift battery will interrupt operations.
Lastly, ensure all employees are trained in the use of appropriate PPE and safety procedures and always choose high-quality chargers and batteries that meet your operational needs and comply with safety standards
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can Forklift Batteries Be Overcharged?
Yes, forklift batteries can be overcharged, which can cause significant damage. Overcharging a lead acid battery leads to excessive heat and the release of hydrogen gas, which can be dangerous. To prevent overcharging, it’s crucial to use chargers with automatic shut-off features. Always monitor the charging process and ensure you are following the manufacturer’s guidelines for charging your specific forklift battery model.
2. How Many Times Can You Charge a Forklift Battery?
A typical lead acid forklift battery can be charged approximately 1,500 times over its lifespan. This equates to about five years if the battery is charged once per workday. The number of charge cycles can vary based on the battery type, charging method, and maintenance practices. Properly managing charge cycles and regular battery maintenance can help maximize the battery life and ensure reliable performance.
相关推荐
- How to Charge Automated Guided Vehicle: Charging AGV Guide
- What is Three Phase Power: Definition, Working Method and Applications
- Industrial Battery Charging: Methods, Best Practices and Safety Precautions
- Is There a Difference Between Industrial Batteries and Regular Consumer Batteries?
- What is an Industrial Battery: Definition, Types, Components & Applications
Search
Recent Posts
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 琼ICP备88888888号