- 【Alltruth Limited】Welcome to Alltruth Power(www.alltruthpower.com), We provide you professional power solutions.
- Make a call:138 5726 9602

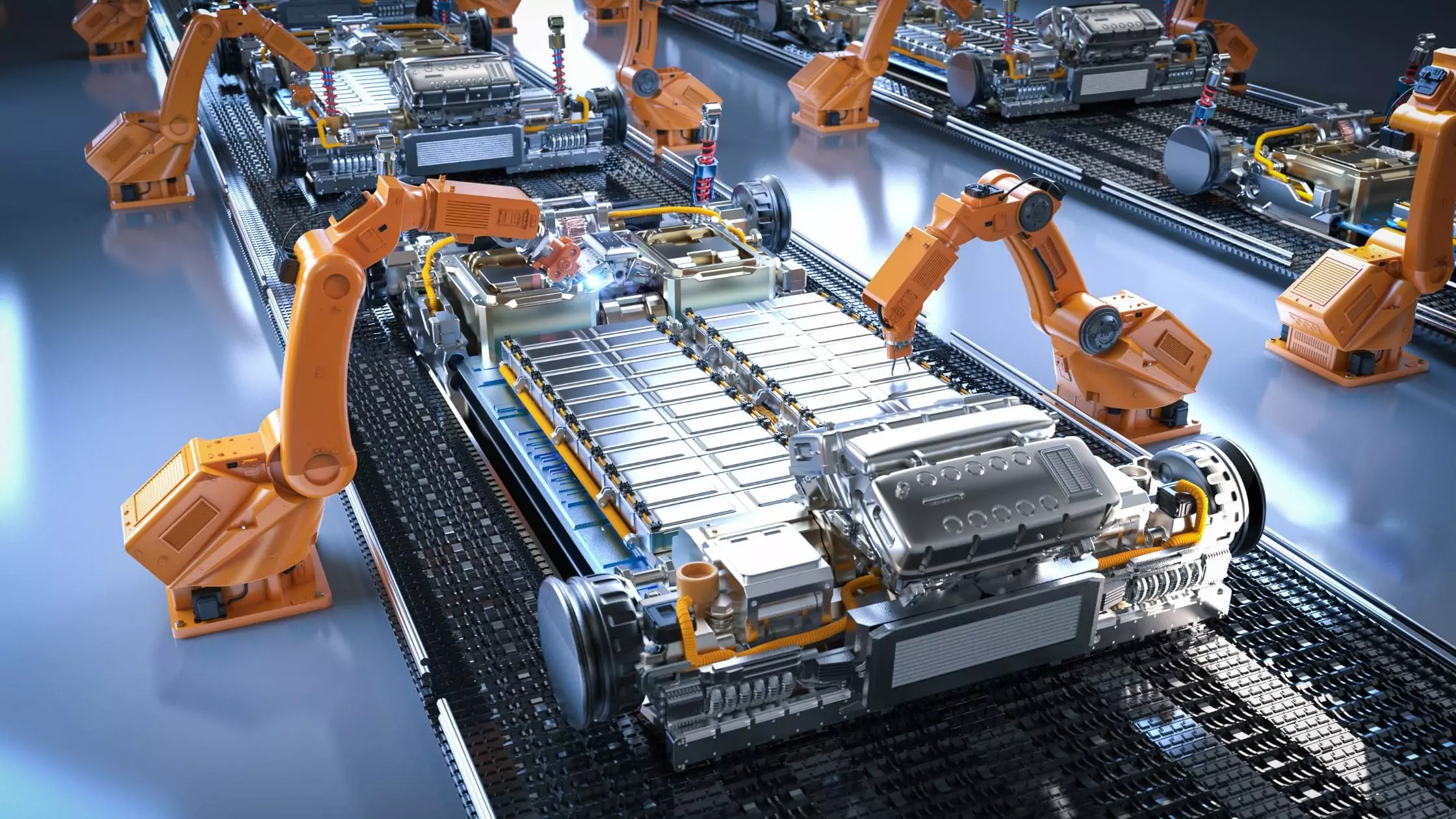
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the importance of reliable power sources cannot be overstated. Industrial batteries, as a cornerstone of this infrastructure, play a key role across various sectors. But what exactly are industrial batteries, and why are they so crucial to modern industry?
What is an Industrial Battery?

An industrial battery is a type of rechargeable battery engineered for robust, reliable performance in demanding industrial applications. This battery type is essential in sectors where high durability and reliability are critical, distinguishing them as a fundamental component in modern industrial operations.
What is the Difference Between Industrial and Consumer Batteries?
The distinction between industrial and consumer batteries lies primarily in their design and intended usage. Industrial batteries are crafted to endure more rigorous conditions and have a higher power-to-size ratio, which is crucial for applications requiring robust energy solutions. They typically feature chemistries that optimize for low self-discharge rates, enhancing their lifespan when not in active use.
Additionally, industrial batteries are designed to resist leakage and can withstand extreme environmental conditions, such as those encountered in medical autoclave sterilization, where high temperature and humidity are prevalent. This makes them well-suited for critical applications in various sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, and heavy machinery.
What Are the Four Main Types of Industrial Batteries?

There are four main types of industrial batteries, including lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries, each distinguished by its chemical composition, typical use cases, and inherent advantages and drawbacks.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the most venerable and commonly used types of industrial batteries, recognized for their reliability and cost-effectiveness. These batteries operate on a simple chemical premise involving lead, lead dioxide, and a sulfuric acid electrolyte solution. Widely utilized in automotive starters, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and emergency lighting systems, their technology is well-established, making them a preferred choice for large-scale energy storage and backup power solutions.
Pros
- Cost-effective: Economically viable for large-scale applications.
- Robustness: Proven technology with a well-understood lifecycle.
- Recyclability: High level of recyclability compared to other battery types.
Cons
- Weight and Size: Heavier and bulkier, requiring significant space.
- Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
- Environmental Impact: Contains toxic substances that require careful disposal.
Nickel-Cadmium Batteries
Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries are known for their robustness and excellent performance under harsh conditions, making them a preferred choice for many industrial applications. These batteries are composed of nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium.
Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and deep discharge cycles makes them ideal for emergency systems, aviation, and railway communications, where reliability is paramount.
Pros
- Durability: NiCd batteries can endure harsh conditions and rough handling.
- Longevity: They offer a high number of charge/discharge cycles.
- Performance: Excellent performance across a wide temperature range.
Cons
- Environmental Concerns: Cadmium is toxic, posing recycling and disposal challenges.
- Memory Effect: They can suffer from memory effects, reducing their efficiency if not properly maintained.
- Cost: Generally more expensive than other types of industrial batteries due to material costs.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are popular in modern applications due to their high energy density and low maintenance requirements. Comprising a lithium compound as the electrode material, lithium batteries are commonly used in mobile devices, electric vehicles, and increasingly in industrial applications requiring high power outputs and longevity.
Pros
- Energy Density: They have a higher energy density, providing longer usage times between charges.
- Low Maintenance: No periodic discharge is needed, and there is no memory effect.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of temperatures and applications.
Cons
- Safety Concerns: Prone to thermal runaway and can pose safety risks if damaged or improperly managed.
- Aging: They degrade over time, even when not in use, affecting their lifespan.
- Cost: High manufacturing cost compared to other battery types due to the use of lithium.
Nickel–Metal Hydride Batteries
Nickel–metal hydride (NiMH) batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that blend reliability with environmental friendliness. They are known for their better energy density compared to nickel-cadmium batteries and are less detrimental to the environment.
NiMH batteries consist of a nickel oxide hydroxide positive electrode and a hydrogen-absorbing alloy for the negative electrode. They are commonly used in applications where weight and space are critical factors, such as in hybrid electric vehicles, medical instruments, and portable power tools. Their ability to be rapidly charged and deliver high power outputs makes them particularly useful in high-demand environments.
Pros
- Environmental Impact: Less toxic than nickel-cadmium batteries, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
- Energy Density: Higher energy density than many other rechargeable batteries, which allows for longer use between charges.
- No Memory Effect: Can be charged or topped off without waiting for a complete discharge, which is advantageous for many industrial applications.
Cons
- Cost: Generally more expensive than nickel-cadmium batteries, which can be a barrier for some businesses.
- Self-Discharge Rate: Higher self-discharge rate than other types of batteries, which may not be ideal for all storage conditions.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Performance can degrade in extremely cold temperatures, which might limit their use in certain geographical areas.
How Does an Industrial Battery Work?

Understanding how industrial batteries store and release energy not only highlights their importance but also aids in optimizing their use in industrial applications.
The Electrochemical Process
The operation of an industrial battery involves complex chemical and physical processes. At the core of these processes is the electrochemical reaction, which allows for the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy, which is then used to power various devices.
Energy Storage and Release
- Chemical Reaction: When a battery is charged, the charger induces a chemical reaction that forces the electric current back into the battery, reversing the discharge reaction and storing energy in chemical form.
- Discharge: During discharge, the chemical process is reversed, releasing the stored energy in the form of electricity.
Components Involved
- Anode and Cathode (Electrodes): These are the sites where the oxidation (anode) and reduction (cathode) reactions occur.
- Electrolyte: A chemical medium that allows the ionic movement necessary for the electrodes’ reactions while prohibiting electron transfer.
- Separator: Serves as a barrier that prevents the electrodes from short-circuiting while allowing the passage of ions.
Key Reactions
- Lead-acid Batteries: The anode reaction produces lead sulfate and electrons, while the cathode uses the electrons to convert lead dioxide into lead sulfate and water, producing energy.
- Lithium-ion Batteries: Lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte and are stored in the cathode; the movement reverses during discharge, releasing energy.
Cycle Life and Efficiency
- Cycle Life: Refers to the number of complete charge and discharge cycles a battery can perform before its capacity falls below a specified percentage of its original capacity.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of a battery involves its ability to convert input energy into useful power output. Factors such as the rate of discharge, the operating temperature, and maintenance quality significantly influence this.
What are the Main Components of an Industrial Battery?
Industrial batteries are complex assemblies made up of several key components, each vital for the battery’s function and efficiency. Understanding these components is essential for anyone involved in the design, use, or maintenance of industrial batteries.
- Cell: The fundamental unit of a battery, the cell is where the chemical reactions occur that generate electricity. Each cell consists of an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. Cells are the primary building blocks of a battery, determining the voltage and capacity of the final product. Cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy through electrochemical reactions.
- Electrodes: Every cell has two electrodes: the anode (negative) and the cathode (positive). Electrodes are crucial for the chemical reactions that produce electricity in batteries. They facilitate the flow of electrons through external circuits, providing power to devices.
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte is critical for the conductivity of ions, which are necessary for the electrochemical reaction. It helps transport ions from one electrode to another, which is essential for maintaining the flow of electrical charge in the battery.
- Separator: A permeable membrane that sits between the anode and cathode. Separators prevent the physical contact between the anode and cathode, which could lead to short circuits. While inhibiting electron flow directly between electrodes, it allows ions to pass through, essential for the reaction.
- Casing: The outer housing of a battery that encloses all internal components. The casing protects the internal components from environmental elements and mechanical damage. The casing also provides structural integrity to the battery, ensuring that the internal structure remains intact and secure.
What Are the Key Features and Parameters of an Industrial Battery?

Understanding key features and parameters of industrial batteries is crucial for selecting the right battery type for specific industrial needs. Here, we explore the essential aspects of capacity, voltage, energy density, and rechargeability that define the performance and suitability of these power sources.
Voltage
Voltage is the electrical potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of a battery. It dictates how much power the battery can deliver to an electrical circuit. Typical voltages for industrial batteries are:
- 12V: Commonly used in backup power systems and smaller machinery.
- 24V: Often found in electric forklifts and other industrial vehicles.
- 48V and above: Used in larger systems, including heavy machinery and energy storage systems for solar and wind applications.
Battery Capacity
Measured in ampere-hours (Ah), capacity indicates the amount of electric charge a battery can deliver at a specified voltage over a period of one hour. This parameter is critical for users to gauge how long a battery will last under specific usage before requiring a recharge.
Higher capacity batteries are capable of powering machinery for longer periods without the need for frequent recharging, which is crucial for minimizing downtime in industrial operations.
Energy Density
Energy density refers to the amount of energy stored in a battery relative to its weight or volume, measured in watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg) or watt-hours per liter (Wh/L). Energy density is a pivotal feature, especially in applications where weight and space are limiting factors.
Batteries with high energy density are ideal for portable industrial equipment and electric vehicles, as they provide longer operation times without adding significant weight or bulk.
Operating Temperature
The operating temperature of a battery is a key parameter that affects its performance, efficiency, and lifespan. Industrial batteries are often subjected to extreme conditions, and their ability to operate effectively within a specific temperature range is critical.
Typical operating temperature ranges for the four main industrial battery types are:
- Lead Acid: -20°C to 50°C
- Nickel Cadmium: -40°C to 60°C
- Lithium-Ion: -20°C to 60°C
- Nickel-Metal Hydride: -20°C to 60°C
What are the Main Applications of Industrial Batteries?
Industrial batteries are utlized across numerous sectors, powering essential systems and devices with reliability and efficiency. Below, we explore eight key industries and environments where these batteries are indispensable, detailing how they contribute to each sector’s operational success.
- Telecommunications: Industrial batteries provide backup power to telecommunications infrastructure, ensuring uninterrupted service during power outages. This is crucial for maintaining communication networks operational, which are essential for emergency services and daily communications.
- Power Utilities: In energy generation and distribution, industrial batteries are used for load leveling and emergency backup. They store excess energy during low demand periods and release it during peak demand times, enhancing grid stability and efficiency.
- Transportation: Batteries power a variety of systems in electric and hybrid vehicles, from starting the engine to powering electrical systems. This includes buses, trains, and fleet vehicles, where consistent and reliable energy supply is critical.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Used in solar and wind installations, industrial batteries store energy generated during peak production times for use during low production periods, facilitating consistent energy supply from intermittent renewable sources.
- Emergency Systems: Industrial batteries are crucial in emergency power systems and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), providing power immediately when primary power sources fail, which is vital for hospitals, data centers, and emergency response operations.
- Material Handling: In warehouses and distribution centers, batteries power forklifts and automated guided vehicles (AGVs), enhancing operational efficiency and worker safety by providing reliable power for heavy lifting and transportation.
- Military Applications: Batteries are used in various military applications, from powering communication equipment to mobile command centers, where reliability can be a matter of national security.
- Medical Equipment: Industrial batteries ensure that critical medical devices such as ventilators, diagnostic equipment, and hospital emergency lighting operate uninterrupted, especially during power outages, ensuring patient care remains unaffected.
What Are the Advantages of Using Industrial Batteries?
Industrial batteries are essential components in numerous sectors due to their robust performance and adaptability. Here are some key advantages that make them invaluable in industrial settings:
- Reliability: Industrial batteries are designed to provide a consistent power supply even under harsh conditions, ensuring that critical systems remain operational at all times.
- Scalability: These batteries can be scaled to meet the energy demands of any size operation, from small workshops to large manufacturing plants, making them versatile for varying industrial needs.
- Environmental Impact: Many industrial batteries, especially newer technologies like lithium-ion, are more environmentally friendly compared to traditional power sources. They offer a cleaner alternative by reducing emissions and, in some cases, are recyclable.
How Much Does an Industrial Battery Cost?

The cost of an industrial battery can cost from $100 to $20000 based on the type, capacity, and intended application.
These prices are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, technological advancements, and supply chain factors. It’s important to contact suppliers or manufacturers for specific quotes based on your exact requirements.
How Long Does an Industrial Battery Last?
Industiral battery lifespan is often measured in charge cycles, with one cycle representing a complete charge and discharge.
The three main factors affecting the lifespan are:
- Usage Patterns: Frequent deep discharges can shorten battery life compared to partial discharges.
- Maintenance Practices: Proper maintenance can significantly extend a battery’s operational life.
- Environmental Conditions: Extreme temperatures and improper storage conditions can degrade battery components faster.
Typical lifespan values for the four battery chemistries in cycles are:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Typically, 500 to 1,000 cycles
- Nickel-Cadmium Batteries: Around 2,000 cycles
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Approximately 1,000 to 2,000 cycles
- Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries: About 500 to 1,000 cycles
How to Store and Maintain an Industrial Battery?
Proper storage and maintenance are crucial for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of industrial batteries. Here are some practical tips:
- Optimal Storage Conditions: Store batteries in a cool, dry place with a stable temperature.Avoid exposing batteries to direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform regular inspections for signs of wear or damage. Keep battery terminals clean and free from corrosion.
- Proper Charging Practices: Use a compatible charger and follow the manufacturer’s charging guidelines. Avoid overcharging, which can lead to reduced battery life and potential safety risks.
- Usage Guidelines: Avoid deep discharges; instead, recharge the battery before it is completely depleted. Regularly cycle the battery to prevent the buildup of crystals on lead-acid types.
- Safety Measures: Always handle batteries with care to avoid punctures or damage to the casing. Ensure that batteries are properly secured and insulated to prevent short circuits.
How to Charge an Industrial Battery?
Proper charging of industrial batteries is crucial to maximize their efficiency and lifespan.
Charging an industrial battery correctly involves using the right industrial battery charger and following specific guidelines to ensure safety and extend the battery’s life. It’s important to charge at the correct voltage and current settings as specified by the manufacturer to avoid overcharging or undercharging, which can damage the battery.
Practical Tips for Safe Charging are:
- Use the Correct Charger: Always use a charger that matches the battery’s specifications. Using an incompatible charger can lead to poor battery performance or even hazards.
- Monitor Temperature: Keep the battery at a stable temperature while charging. Excessive heat can lead to battery degradation, so ensure the charging area is well-ventilated.
- Avoid Overcharging: Overcharging can reduce a battery’s lifespan. Most modern chargers have automatic cutoffs to prevent this, but it’s crucial to monitor the battery’s voltage.
- Charge in a Safe Location: Charge batteries away from flammable materials. Charging areas should be free of moisture and extreme temperatures.
Common Charging Methods
- Standard Charging: Involves charging the battery at a fixed rate until it reaches full capacity. This method is suitable for daily use.
- Trickle Charging: Used to keep a fully charged battery in a ready state without overcharging. It’s ideal for batteries in backup power systems.
- Fast Charging: Useful when time is critical. This method charges batteries quickly at a high rate but should be monitored closely to avoid damaging the battery.
Importance of Choosing Quality Industrial Battery Chargers
Selecting a high-quality charger is as crucial as the battery itself. Quality chargers adjust to the battery’s needs, enhance battery efficiency, and extend its service life. Essential features to look for in a charger include:
- Automatic Voltage Adjustment: Ensures the battery is charged optimally depending on its capacity and current charge level.
- Built-in Safety Features: Overcharge protection, temperature control, and short circuit prevention are critical for safe operation.
- Durability and Reliability: Choose chargers that are robust and can withstand the tough conditions of industrial environments.
What are Some Potential Industrial Battery Hazards?
Industrial batteries are crucial for many applications, but they carry risks if not handled or maintained properly. Understanding these risks and how to mitigate them is essential for safety.
- Chemical Exposure: Industrial batteries, such as lead-acid and nickel-cadmium, contain hazardous materials that can cause severe harm if they leak or if the battery casing is damaged. Exposure to battery acid can lead to chemical burns, while cadmium is a toxic heavy metal linked to various health issues.
- Fire and Explosion Risks: Batteries store a large amount of energy and can catch fire or explode if improperly managed. Overcharging, short-circuiting, or physical damage can lead to thermal runaway, where increasing temperatures lead to further chemical reactions that release more heat.
- Environmental Hazards: Improper disposal of industrial batteries can lead to heavy metals and other toxic substances leaching into the environment, contaminating soil and water sources.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
To mitigate these hazards, strict regulations and best practices must be followed:
- Proper Handling: Always handle batteries with care to prevent punctures or damage to the casing. Use tools designed for working with batteries to avoid accidental short circuits.
- Appropriate Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from combustible materials. Ensure good ventilation to prevent the buildup of gases released during charging.
- Regular Maintenance: Inspect batteries regularly for signs of damage or leakage. Check connections and cables for wear and ensure they are tight and corrosion-free.
- Recycling and Disposal: Follow local regulations for the disposal of industrial batteries. Many regions require batteries to be recycled to prevent environmental contamination and recover valuable materials.
- Prevent Accidental Circuits: Never allow metal objects to bridge the terminals of a battery, which can create a dangerous short circuit.
- Wear Protective Gear: When working with batteries, wear protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection to guard against chemical exposure.
- Use Correct Tools: Employ non-conductive tools to prevent accidental sparks or shorts when working on battery installations.
- Power Management: Always turn off chargers and disconnect power before connecting or disconnecting batteries to prevent sparks and potential explosions.
- Vent Plug Management: Keep vent plugs in place to prevent the escape of gases, except when servicing the battery, such as topping up water in lead-acid batteries.
How to Choose the Right Industrial Battery?

Choosing the right industrial battery involves a detailed assessment of your needs, a comparison of battery types, and consideration of long-term usability.
Below, we explore several scenarios to guide you in selecting the best industrial battery for your specific applications.
- Operational Requirements: Consider the energy requirements of your application. Does your operation require continuous power supply, or can it handle intermittent downtimes? For continuous operations, batteries with a longer service life and higher energy density, such as lithium-ion batteries, might be necessary.
- Environmental Conditions: Evaluate the environmental conditions in which the batteries will operate. High temperatures can affect battery life and performance, making some chemistries, like nickel-metal hydride, less suitable due to their sensitivity to temperature fluctuations.
- Physical Space: Determine the physical space available for the battery installation. Some battery types, such as lead-acid, are bulkier and may require more space, whereas lithium-ion batteries are more compact and versatile in form factor.
Scenario 1
Data Center UPS: A data center requires an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to prevent data loss during power outages.
Recommended Battery: Lithium-ion due to its high energy density and reliability. Lithium-ion batteries can provide power ranging from 100 Ah to 1000 Ah, suitable for maintaining operations during short to medium duration outages.
Scenario 2
Remote Telecommunication Towers: These installations often face extreme temperatures and accessibility issues.
Recommended Battery: Nickel-cadmium batteries are ideal due to their excellent performance in temperature extremes and durability. Nickel-cadmium batteries can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 60°C, ensuring reliable performance in isolated environments.
Scenario 3
Electric Forklifts in Warehouses: Require batteries that can withstand frequent charging and discharging cycles.
Recommended Battery: Lead-acid batteries are preferred for their ability to deliver consistent power output and their cost-effectiveness in stationary applications. Lead-acid batteries typically last for 1,000 to 1,500 cycles, suitable for daily operations in a warehouse setting.
Assessing Vendor Claims and Specifications
When selecting a battery, it’s crucial to scrutinize vendor claims and specifications to match your operational requirements. Here are some tips on what to look for and questions to ask:
- Capacity and Energy Density: Verify the energy density and capacity claims. How do they measure up against your energy requirements?
- Cycle Life and Longevity: Ask for detailed data on cycle life based on real-world application scenarios similar to yours.
- Safety Features: What safety mechanisms are in place? Look for certifications and safety test results.
- Warranty and Support: Evaluate the warranty length and what it covers. Understand the type of support (e.g., onsite, remote) available post-purchase.
- Vendor Reputation and Reviews: Research customer feedback and case studies. How reliable is the vendor in long-term engagements?
- Cost Comparison: Beyond the upfront cost, consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, replacement, and disposal.
Questions to Ask Vendors
- Can you provide references or case studies from businesses in similar industries using your batteries?
- What are the expected maintenance requirements and associated costs?
- How does your battery technology handle extreme operational conditions like high temperatures or vibrations?
- What are the environmental impacts of your batteries, and how can they be mitigated through recycling or other means?
What are Future Trends in Industrial Battery Technology?
Exploring the future of industrial battery technology unveils a panorama of innovations poised to transform energy storage and its application across various industries. This section delves into the upcoming changes, focusing on advancements in battery chemistry, and evaluates their potential impacts.
Advancements in Battery Chemistry
The relentless pursuit of more efficient, durable, and cost-effective battery solutions has led to significant research and development in battery chemistry. Innovations in this field are not just enhancing the performance of batteries but are also paving the way for more sustainable energy solutions. Here are some of the key advancements:
- Solid-State Batteries: Moving away from liquid electrolytes, the development of solid-state batteries promises higher energy densities and improved safety profiles. Solid electrolytes are less prone to leaking and can operate more effectively at higher temperatures.
- Lithium-Sulfur Batteries: With a higher energy density than traditional lithium-ion batteries, lithium-sulfur technology is under development, aiming to extend the battery life and reduce costs significantly. This technology could revolutionize sectors like electric vehicles and aviation by providing longer flight and drive ranges.
- Advanced Lead-Acid Technology: Enhancements in lead-acid batteries, such as carbon additives to electrodes and improved valve designs, are increasing their efficiency and lifecycle, making them more competitive with more modern technologies.
- Silicon Anodes: Silicon anodes are being developed to replace graphite in lithium-ion batteries, potentially tripling the energy density while reducing costs. This advancement could lead to longer-lasting batteries for devices and vehicles.
Conclusion
The ongoing advancements in battery chemistry are setting the stage for a revolution in how energy is stored and utilized across industries. This shift not only promises to enhance the efficiency and performance of batteries but also plays a critical role in the global transition towards renewable energy sources.
Industrial batteries are becoming increasingly important, not just in powering devices and machinery, but in enabling a sustainable future. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will provide the backbone for a range of applications, driving forward innovations that will fundamentally change our approach to energy consumption and management.
相关推荐
- Forklift Charging: How to Charge a Forklift and Tips When Choosing a Forklift Battery Charging System
- How to Charge Automated Guided Vehicle: Charging AGV Guide
- What is Three Phase Power: Definition, Working Method and Applications
- Industrial Battery Charging: Methods, Best Practices and Safety Precautions
- Is There a Difference Between Industrial Batteries and Regular Consumer Batteries?
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 琼ICP备88888888号